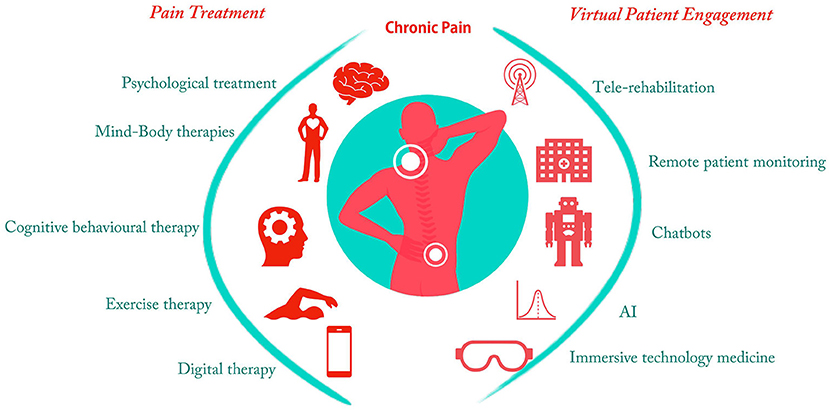
Chronic pain, defined as persistent discomfort lasting beyond the typical healing period, affects millions worldwide, significantly diminishing quality of life. Effective management is crucial to enhance daily functioning and overall well-being. This article explores contemporary strategies for managing chronic pain, supported by verified sources.
1. Pharmacological Treatments
- Non-Opioid Analgesics: Medications such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed for chronic pain management due to their efficacy and lower risk profiles compared to opioids.
- Antidepressants and Anticonvulsants: Certain antidepressants and anticonvulsant medications have been found effective in treating neuropathic pain by modulating pain pathways in the nervous system.
2. Non-Pharmacological Therapies
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in tailored exercise programs can improve mobility and reduce pain intensity. Physical therapists design regimens that enhance strength and flexibility, aiding in pain management.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT addresses the psychological aspects of chronic pain, helping patients develop coping strategies to manage pain-related thoughts and behaviors.
- Acupuncture and Massage Therapy: These alternative therapies have shown promise in alleviating chronic pain by stimulating the body’s natural pain-relieving mechanisms.
3. Interventional Procedures
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): RFA involves using heat to disrupt nerve signals responsible for pain, providing relief for certain chronic pain conditions.
- Nerve Blocks and Injections: Administering anesthetic or steroid injections near specific nerves can offer temporary relief for chronic pain sufferers.
4. Emerging Therapies
- Scrambler Therapy: This non-invasive treatment reprograms nerve pathways to reduce pain perception and has shown promising results in clinical studies.
- Pain Reprocessing Therapy: A behavioral approach that helps patients reinterpret pain signals, aiming to reduce or eliminate chronic pain by altering neural pathways.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
- Diet and Nutrition: Adhering to a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can reduce inflammation and alleviate chronic pain. Recent studies suggest that dietary choices play a significant role in pain management.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in consistent physical activity helps maintain joint function and releases endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers.
6. Multidisciplinary Approach
Combining various treatment modalities often yields the best results. A comprehensive pain management plan may include medical treatments, physical therapy, psychological support, and lifestyle changes tailored to the individual’s needs.
In conclusion, managing chronic pain requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both physical and psychological components. Consulting with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized pain management plan is essential for effective relief and improved quality of life.