Understanding Antibiotics: What You Need to Know
Antibiotics are among the most widely prescribed medications in the world, but despite their popularity, many people are unclear about how they work, when they should be used, and what potential risks they pose. Whether you’re taking antibiotics for an infection or just want to learn more about these powerful drugs, it’s essential to understand how antibiotics function, their benefits, and their limitations.
At Relieve Pharmacy, we believe in educating our community so you can make informed decisions about your health. In this blog post, we’ll explore everything you need to know about antibiotics, their proper use, and how to avoid misuse.
What Are Antibiotics?
Antibiotics are medications designed to treat bacterial infections. They work by either killing bacteria or inhibiting their growth, allowing your body’s immune system to fight the infection more effectively. Antibiotics are not effective against viral infections such as the flu, cold, or COVID-19, and taking them for viral illnesses is both ineffective and harmful.
There are various types of antibiotics, including:
- Penicillins: Often used for skin infections, respiratory infections, and urinary tract infections.
- Macrolides: Commonly prescribed for respiratory infections, such as pneumonia or bronchitis.
- Tetracyclines: Used for treating acne, respiratory infections, and Lyme disease.
- Fluoroquinolones: Typically used for urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and some gastrointestinal infections.
When Are Antibiotics Necessary?
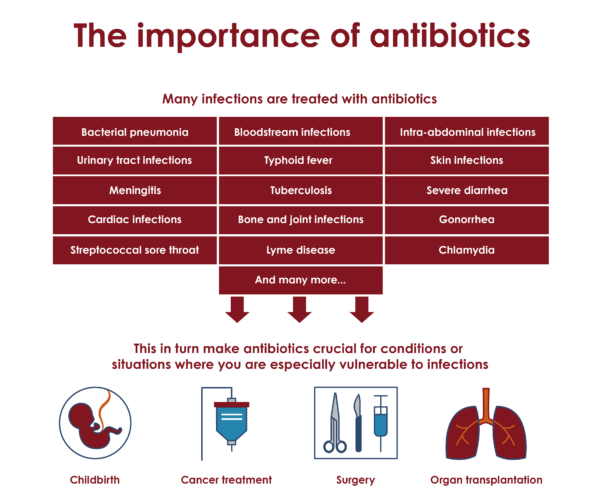
Antibiotics are essential in treating bacterial infections, but they are not a catch-all solution. They are necessary in situations such as:
- Bacterial pneumonia
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Strep throat
- Skin infections (like cellulitis)
- Ear infections caused by bacteria
However, antibiotics are not effective against viral infections such as:
- Common colds
- Flu
- COVID-19
- Most cases of bronchitis and sore throats
Using antibiotics when they’re not needed can lead to serious consequences, including antibiotic resistance, which occurs when bacteria evolve to resist the drugs designed to kill them.
- Further Reading: CDC on the Importance of Correct Antibiotic Use
How Do Antibiotics Work?
Antibiotics target specific aspects of bacterial cells that are not present in human cells, making them highly effective at treating bacterial infections while minimizing harm to the body. There are two main ways antibiotics work:
- Bactericidal Antibiotics: These antibiotics kill bacteria directly. Penicillin and amoxicillin are examples of bactericidal antibiotics.
- Bacteriostatic Antibiotics: These antibiotics inhibit the growth and reproduction of bacteria, allowing the immune system to take over and fight the infection. Erythromycin is an example of a bacteriostatic antibiotic.
By targeting the bacterial structure, antibiotics help stop the infection from spreading and help your body recover.
- More Information: Mayo Clinic on How Antibiotics Work
The Risks of Overusing Antibiotics
While antibiotics can be life-saving, their overuse and misuse pose serious health risks. The most significant concern is antibiotic resistance, which occurs when bacteria evolve to become resistant to the drugs that once killed them. This makes infections harder to treat and increases the risk of complications.
Antibiotic resistance is a growing public health concern, and health organizations worldwide are working to raise awareness about the dangers of overprescribing antibiotics.
How to Prevent Antibiotic Resistance:
- Only take antibiotics when prescribed by a healthcare professional.
- Never share your antibiotics with others, even if they have similar symptoms.
- Complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if you start feeling better before finishing the medication.
- Do not pressure your doctor into prescribing antibiotics for viral infections like the flu or cold.
- Learn More: World Health Organization on Antibiotic Resistance
Side Effects of Antibiotics
While antibiotics are generally safe when used correctly, they can cause side effects. Some common side effects include:
- Upset stomach or diarrhea: Many antibiotics can irritate your digestive system.
- Allergic reactions: Some people may develop rashes, swelling, or difficulty breathing, especially when taking penicillin or cephalosporins.
- Yeast infections: Antibiotics can disrupt the balance of bacteria in the body, leading to an overgrowth of yeast in the mouth or genital area.
If you experience any severe side effects, such as difficulty breathing or swelling of the face and throat, seek immediate medical attention. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist if you’re unsure about side effects or how to manage them.
- More on Side Effects: FDA Guide to Antibiotic Side Effects
Best Practices for Taking Antibiotics
To ensure that you’re getting the most benefit from your antibiotics and minimizing risks, follow these best practices:
- Take antibiotics as prescribed: Follow the dosage and frequency exactly as instructed by your healthcare provider.
- Finish the entire course: Even if you feel better before finishing the medication, it’s important to complete the entire course to prevent the infection from coming back and to avoid developing antibiotic resistance.
- Avoid alcohol: Some antibiotics can interact with alcohol and cause nausea, vomiting, or other side effects. Check with your pharmacist or healthcare provider about any restrictions on alcohol.
- Watch for interactions: Some medications and supplements can interact with antibiotics, making them less effective or increasing the risk of side effects. Always inform your healthcare provider about all medications you’re taking.
- Antibiotic Adherence Tips: CDC on Proper Antibiotic Use
When Should You Contact Your Healthcare Provider?
If you experience unexpected side effects or if your symptoms worsen despite taking antibiotics, reach out to your healthcare provider. You may need a different antibiotic or further evaluation to ensure the infection is being treated properly.
It’s especially important to contact your doctor if you:
- Develop a rash, swelling, or difficulty breathing (signs of an allergic reaction).
- Experience severe diarrhea or blood in your stool.
- Notice unusual symptoms like joint pain or changes in vision.
Early intervention can help prevent complications and ensure the most effective treatment for your condition.
Conclusion
Antibiotics are a powerful tool in the fight against bacterial infections, but they must be used responsibly. By understanding how antibiotics work, when to use them, and the risks associated with misuse, you can protect your health and help prevent the growing issue of antibiotic resistance.
At Relieve Pharmacy, we’re here to help you navigate the world of antibiotics and other medications. If you have any questions or need advice on your prescription, don’t hesitate to contact us or speak with one of our pharmacists.