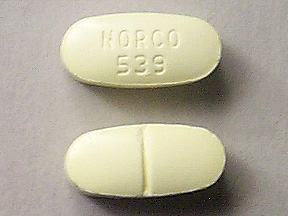
Hydrocodone 5mg/325mg: Comprehensive Guide and Dosage Information
Hydrocodone 5mg/325mg, also known as 5mg 325mg hydrocodone, combines 5mg of hydrocodone with 325mg of acetaminophen in each tablet. This prescription medication is designed to manage moderate to severe pain effectively. Hydrocodone is an opioid analgesic, while acetaminophen is a non-opioid pain reliever that enhances the overall pain relief.
Indication
Hydrocodone 5mg/325mg is prescribed for short-term relief of moderate to severe pain. It is commonly used following surgeries, injuries, or other conditions that cause significant discomfort. This combination is not intended for chronic pain management or long-term use.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of Hydrocodone 5mg/325mg should be individualized based on the patient’s pain level, opioid tolerance, and overall health. Follow these general dosing guidelines:
- Starting Dose: For adults, the typical starting dose is 1 tablet every 4 to 6 hours as needed for pain relief. The exact dosage may vary based on pain severity and individual response.
- Titration: Adjust the dose cautiously to achieve effective pain control while minimizing side effects. Do not exceed the maximum recommended dose of 6 tablets per day.
- Maintenance Dose: Regular monitoring is essential to ensure that the medication provides adequate pain relief. Dosage adjustments should be made based on the patient’s ongoing pain management needs.
- Discontinuation: To avoid withdrawal symptoms, taper the dosage of Hydrocodone 5mg/325mg gradually rather than stopping abruptly. Consult with a healthcare provider for a proper tapering plan.
Administration
- Form: Hydrocodone 5mg/325mg is available in tablet form.
- Method: Swallow the tablet whole with water. Do not crush, chew, or dissolve the tablet, as this can lead to a rapid release of hydrocodone and increase the risk of overdose.
- Timing: Administer the medication every 4 to 6 hours as needed for pain. Adhere to the prescribed schedule to ensure consistent pain relief.
Precautions
- Risk of Abuse: Hydrocodone 5mg/325mg has a high potential for abuse, addiction, and misuse. Use this medication strictly as prescribed and monitor for any signs of misuse.
- Renal and Hepatic Function: Dose adjustments may be necessary for patients with impaired kidney or liver function to avoid adverse effects.
- Drug Interactions: Be aware of potential interactions with other central nervous system depressants, as these can increase the risk of severe side effects, including respiratory depression.
Side Effects
Common side effects of Hydrocodone 5mg/325mg include constipation, nausea, dizziness, and drowsiness. Serious side effects that require immediate medical attention include respiratory depression, severe allergic reactions, and significant hypotension.
Conclusion
Hydrocodone 5mg/325mg, also referred to as 5mg 325mg hydrocodone or hydrocodone 5mg/acetaminophen 325mg tab, is an effective medication for managing moderate to severe pain. Adherence to dosing guidelines is crucial for achieving optimal pain relief while minimizing risks. For purchasing Hydrocodone 5mg/325mg, a valid prescription from a licensed healthcare provider is necessary.
For more information or to purchase Hydrocodone 5mg/325mg, consult your healthcare provider or visit your local pharmacy. Always follow medical advice and dosage instructions to ensure safe and effective use of this medication.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.